Medical
Services
We believe that everyone has the right to feel confident in their skin. At Art of SKIN Dermatology, Laser and Cosmetic Surgery, we offer professional diagnosis and advanced treatment for a wide variety of medical diseases and conditions affecting the skin, hair, and nails.

Dr. Lubitz
Dr. Lubitz is an accredited Dermatologist with the Royal College of Physicians and Surgeons of Canada and the American Board of Dermatology. As a professionally trained, skilled and experienced skin specialist, he is able to effectively diagnose and treat your skin disease, including conditions affecting your hair and nails.
Dr. Lubitz is well-trained and experienced in treating different blood vessel conditions, including varicose, dilated, and spider veins. He offers a variety of advanced treatment options, including laser therapy, sclerotherapy, and surgical removal. Dr. Lubitz offers a specialized Vein Clinic for patients with vein problems localized to the lower extremities. If you are concerned about blood vessels and want to learn more about your treatment options, request a consultation in our Vein Clinic (lower extremity veins) or our Cosmetic Clinic (veins located in all other areas of the body).
Please note: Patients wanting to see Dr. Lubitz for medical reasons are required to have a medical referral from a physician prior to their appointment. This is usually from their family physician but it can be from any physician or accredited healthcare professional. Alberta Health Care (AHC) does not cover all treatments for all medical conditions. The cost of some medical treatments will be the responsibility of the patient.

Varicose Veins
Veins carry oxygen-depleted blood back to the heart. If the walls of the blood vessels weaken or there is increased backward pressure in the vessel blood can back up or pool inside the vein. This results in gradual distension of the vein, causing the development of reticular veins and varicose veins —enlarged, dilated blood vessels, purplish or bluish in colour, which may bulge above the skin’s surface, commonly seen in the legs. Reticular and varicose veins may cause discomfort, swelling, or even pain in the affected area.
Patients with varicose veins in their lower extremities are at a greater risk for clots forming in their legs, referred to as deep vein thrombosis (DVT). These clots can dislodge into the body’s main circulation and cause clots in the lungs or brain.
Factors that may contribute to the development of varicose, reticular and spider veins (very small vessels) appearing on the lower extremities include heredity, age, pregnancy, previous trauma to the extremity, obesity, heart disease, chronic diseases and standing or sitting for long periods of time, particularly with the legs crossed.
Chronic moderate or severe vein disease of the lower extremities significantly reduces mobility. It results in a condition called stasis dermatitis and places the patient at risk for infections, ulcers and poor wound healing.
Patients with dilated reticular veins or varicose veins often benefit from wearing compression stockings to improve the return of blood in their veins from the lower extremities.
Dermatologists are specialists trained to diagnose and treat the different types of vein disease. A consultation with a dermatologist can help to diagnose the particular type of vein disease a patient might have, to educate the patient as to what can be done to minimize the damage moving forward, and to review the different treatment options available.
Why You Need Treatment
Large varicose veins, particularly those located high in the thigh and groin, can be treated by surgical stripping. Surgical stripping is an older technique but is still applicable in some situations and is often associated with significant recovery time. Today, these large vessels are commonly treated safely and effectively with less downtime using a laser (YAG or EVLA – endovenous laser ablation) or ultrasound guided foam sclerotherapy.
Today the most common treatment for the majority of dilated reticular veins and varicose veins is sclerotherapy. Sclerotherapy refers to the injection of a solution, either liquid or foam, into the vein, causing it to collapse and eventually be reabsorbed by the body.
Laser vein therapies using a YAG for reticular veins or Endovenous Laser Ablation (EVLA) for varicose veins are safe and effective treatment options. These offer a minimally invasive laser treatment to seal off damaged veins, diverting blood flow to healthy veins.
Spider Veins or Spider Vessels
Spider veins or spider vessels (also called telangiectasia) are small, dilated blood vessels (veins or capillaries) that appear close to the skin’s surface, mostly on the legs, face, chest and hands. They cause no discomfort and are primarily of cosmetic concern. They can bleed significantly if traumatized. Spider veins are commonly treated using Sclerotherapy or Laser therapy.
Different Medical Services
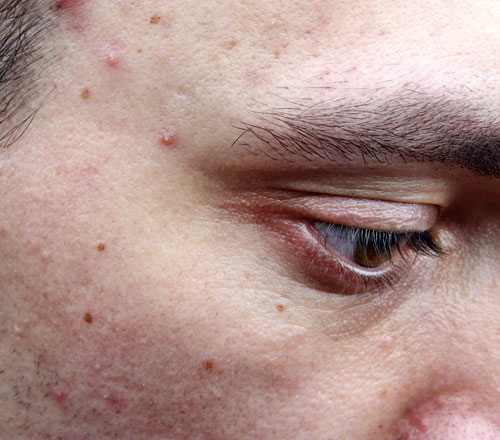
Acne
Acne (acne vulgaris) is a common, often chronic skin problem that affects many teenagers and a significant number of adults. While acne is slightly more common, particularly the severe type, in males during the teenage years, in adulthood, acne affects more females and often for a longer period of time.
Acne can appear in many forms: as blackheads, whiteheads, inflamed pimples or larger, painful cysts. The root cause of acne is the abnormal development and function of cells inside the skin’s hair follicles and oil glands. This leads to the clogging of oil glands associated with hair follicles, the failure to deliver oils (sebum) to the skin’s surface, and the buildup of bacteria within the gland, which results in inflammation and the development of the acne lesion.
Patients with acne are often teased about their appearance (particularly in adolescence), they may feel undesirable or unattractive, and can suffer from varying degrees of decreased self esteem, anxiety, depression, and even become antisocial. Untreated or mistreated acne can result in permanent scarring, which can lead to further decreases in self-esteem and self worth that can last well into adulthood.
Fortunately, patients do not need to suffer from acne. Acne can be successfully and safely treated in virtually all cases. However, it is important that the correct diagnosis be made and that the appropriate treatment be initiated early on in the course of the condition in order to avoid potentially permanent consequences.
Patients with acne are best examined and treated by an accredited dermatologist, a skin specialist, who is appropriately trained to diagnose and treat acne in a safe and effective manner.
Dr. Lubitz has a special interest in acne and acne scarring and has more than 20 years of experience in treating the varying kinds of acne situations. He is very well trained and knowledgeable in the most advanced treatment options available for this condition.
At Art of SKIN Dermatology, Laser and Cosmetic Surgery, treating acne is one of our specialities. There are many very successful and safe treatment options for acne, including medical and nonmedical options. Some medical examples include oral and topical medications in addition to several non-drug treatments including lasers, light therapy, chemical peels and medical grade cosmeceuticals (skin care products). Our skin care specialists can review the different acne treatments available in addition to guiding patients to help them understand how appropriate skin care can help keep their acne under control.
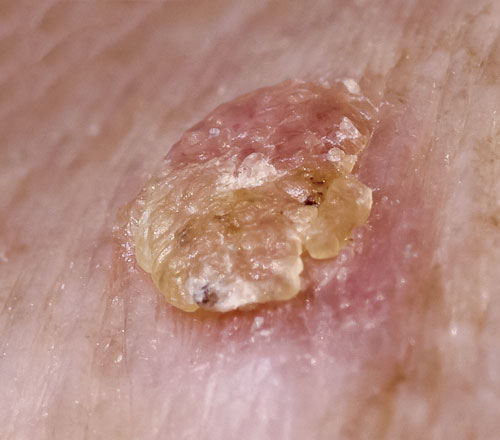
Actinic Keratosis

Alopecia
Alopecia refers to medically-related hair loss. Alopecia, in most cases, does not pose significant health risks by itself, except for an increased risk of skin cancer on the scalp in patients who have lost their scalp hair due to increased exposure to UV light. However, many people seek treatment for their alopecia because of the social stigma associated with irregular or premature hair loss.
There are several different types of hair loss, including androgenic alopecia, alopecia areata, scarring alopecia, and telogen effluvium. The causes and treatments for the different types of alopecia are specific for that type of hair loss.
For example, with respect to alopecia areata, while we don’t fully understand this type of alopecia, we do understand that it occurs when the immune system attacks the hair follicles (structures that contain the roots of the hair), causing either temporary or permanent hair loss. Hair loss with alopecia areata can occur on the head or anywhere on the body.
There are a variety of treatment options for alopecia areata, some medical and some cosmetic.
Medical treatment options include:
- Topical and oral medications
- Intralesional and intramuscular cortisone injections
- Immunotherapy that helps hair to grow (DPC)
Different types of alopecia have different treatment options; the best treatment option will depend not only on the patient’s particular presentation but also on the particular condition being treated.
Dermatologists are specially trained to diagnose and treat disorders of the hair such as the different types of alopecia, in addition to diseases of the skin and nails.
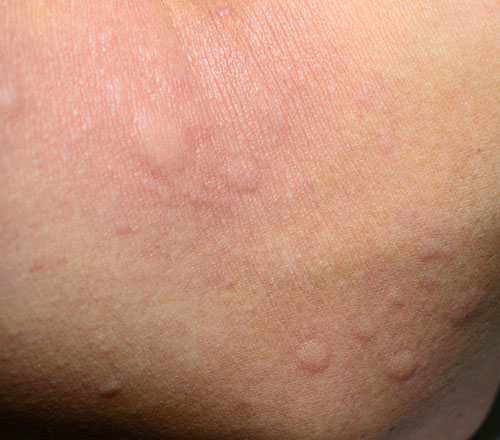
Contact Dermatitis
Contact dermatitis is a rash that develops after your skin has touched or come into contact with a particular chemical. There are two types of contact dermatitis, which can occur simultaneously in a patient. These include:
- Allergic Contact Dermatitis is a rash caused when you come into contact with something that you are allergic to, such as latex gloves, hair dye, and makeup or nail products.
- Irritant Contact Dermatitis develops from too much exposure to something that is irritating to the skin, such as chemicals or detergents.
Environmental factors such as the extreme dryness that we have in Alberta or less common factors such as too much exposure to water can contribute to irritant contact dermatitis. Diaper rash is a common example where a baby’s skin is easily irritated by a soiled diaper.

Dilated Pores
There are multiple treatment options for dilated pores, including:
- Topical medical treatment with a retinoid
- Punch grafting
- Surgical excision of individual lesions.
Widespread areas of skin with dilated pores can be improved by using various cosmetic treatments, including:
- Fractionated CO2 laser
- Chemical peeling techniques

Hair Disorders
There are many types of hair disorders, and they can be caused by different factors. Hair disorders can be genetically inherited or acquired. Also, they may involve abnormalities of hair shaft growth, some involve hair shaft composition, and several hair disorders result from infection or systemic diseases.
An accredited dermatologist is specially trained to diagnose and treat the vast spectrum of hair disorders.
- Hair loss (alopecia)
- Hair growth, including hypertrichosis and hirsutism
- Hair shaft abnormalities – hair brittleness, breakage, colour change
- Hair disorders or scalp conditions caused by systemic diseases, such as, psoriasis, lichen planus, lupus erythematosus, contact dermatitis, and seborrheic dermatitis.

Hyperhidrosis
The use of Neuromodulators is a relatively new (i.e., within the last 15 years) and exciting treatment for hyperhidrosis. Neuromodulators, such as Botox™, can be safely used to successfully treat hyperhidrosis in most commonly affected areas with often life changing, results for many patients.
Learn about Botox as a treatment option for hyperhidrosis at Art of SKIN Dermatology, Laser and Cosmetic Surgery.

Lupus Erythematosus
Lupus is one of many immune system disorders, also known as autoimmune or collagen vascular diseases. In autoimmune diseases, the immune system turns against the body, leading to inflammation and damage to various body tissues. Lupus can affect many parts of the body, including the skin.
Although people with this disease may have many different symptoms, some of the most common symptoms include:
- Extreme fatigue
- Painful or swollen joints
- Unexplained fever
- Skin rashes, made worse by sun exposure.
- Kidney problems
- Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is the most serious form of the disease.
- Discoid lupus erythematosus (DLE), is a chronic skin disorder in which red, raised lesions appear on the face, scalp, or elsewhere on the skin. The raised areas may become thick and scaly and may cause scarring. Lupus may also cause hair loss, thinning, or breakage. Also, Lupus may cause the hair to become brittle and fall out in particular patches.
- Subacute Cutaneous Lupus, Bullous Lupus, Lupus Profundus, Drug Induced Lupus and Neonatal Lupus are less common variants.
Lupus may also cause hair loss, thinning or breakage. Hair may become brittle and fall out in particular patches.

Melasma
Melasma is a common skin pigmentation disorder. It is more common in women than men and people with darker skin types. Melasma appears most commonly on the face as brownish patches, although it can occur on the neck, chest, and arms. The disorder is triggered by hormones (especially estrogen or estrogen derivatives) and is worsened by unprotected or excessive exposure to the sun.
It is critically important for patients with melasma to keep their skin protected using sunscreen and a hat when exposed to UV light. Melasma is commonly seen in pregnant women, hence the term “mask of pregnancy.” Some medications, such as birth control pills (especially those containing estrogen), can also contribute to melasma. As there are several different skin disorders that present with pigmentation changes, it is important that the correct diagnosis be made. A dermatologist can help diagnose, provide relevant education, and effective treatment for this common but frustrating skin disorder.
Melasma may fade on its own over time, but unfortunately this is usually not the case. Melasma in most cases gradually becomes permanent and progressive. If or when it does become permanent, there are several effective treatments available.
Hydroquinone
Hydroquinone is a topical medicine that is applied to the skin. It works by turning off the pigmentation production mechanism; thus, lightening the skin. This treatment may come as a cream, lotion, gel, or liquid. You may be able to access products containing hydroquinone without a prescription; however, they will contain less hydroquinone and often will be less stable and predictable than a product that your dermatologist can prescribe or recommend.
Tretinoin and Corticosteroids
Tretinoin and corticosteroids are topical medicines that your dermatologist may prescribe to enhance the skin lightening process. Oftentimes, your dermatologist will suggest a supplementary all-in-one cream that contains hydroquinone, tretinoin, and a corticosteroid that works better than using a cream where each ingredient is applied separately.
Other Topical Medications
Your dermatologist may prescribe other topical treatments, either alone or in combination with other treatments, such as Azelaic acid or Kojic acid to help lighten the pigmentation associated with melasma.
Cosmetic Treatments for Melasma
In most cases, melasma can be improved cosmetically using various skin procedures, such as:
- TCA chemical peeling
- Obagi Skin Restoration Protocol
- Lasers; however, special care needs to be taken as some lasers can contribute to rebound and increased pigmentation.
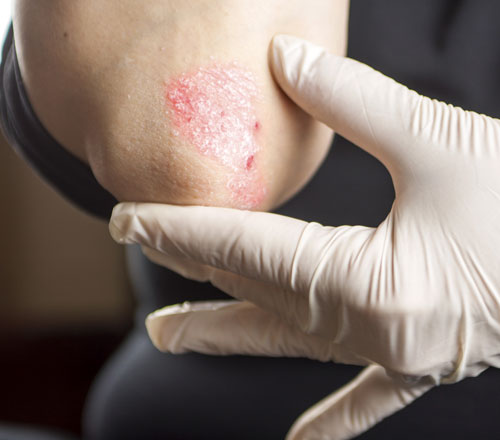
Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a common chronic skin disease affecting upwards of 1% of Canadians. It is an immune-mediated disease that causes the skin cells to grow too quickly. The body cannot shed these skin cells, causing them to accumulate on the skin’s surface. Psoriasis may also affect how a person’s nails look and feel. In some cases, psoriasis can cause pitted and deformed nails that are thickened and discoloured, or nails that separate from the nail bed.
Psoriasis commonly affects the scalp. Psoriasis of the scalp can cause scaly patches, flaking and itching. Inflammation from psoriasis, scratching, harsh treatments and the psychological stress from the disease can also lead to temporary hair loss. Psoriasis can also affect the joints of the body, resulting in inflammation, pain, loss of mobility and potentially permanent damage.
A wide variety of topical, systemic and light-based therapies are available to effectively and safely treat the different types of psoriasis. The correct diagnosis of psoriasis must be made early so the patient can be treated appropriately and promptly. Patients with this disease would benefit from early assessments and treatment from a dermatologist. A dermatologist is an accredited skin specialist trained in assessing and diagnosing psoriasis, in addition to being skilled in administering the most up-to-date treatment options.

Rosacea
Rosacea (full name: Erythrotelangiectatic Acne Rosacea) is a common, chronic skin problem characterized by increased facial redness, dilated blood vessels, called telangiectasia, skin sensitivity and inflammatory acne-like skin lesions. This disease most commonly affects the nose, chin, and cheeks. Rosacea is more common in people of fairer skin types, particularly individuals of British Isle or Northern European descent. If left untreated, rosacea worsens over time. In some cases, disfiguring and permanent soft tissue enlargement of the nose, known as rhinophyma, can occur, particularly in men.
Taking the necessary precautions associated with sun exposure is essential, as excessive and unprotected sun exposure can contribute to disease progression. Common triggers of rosacea include extreme temperatures, strong wind, sun exposure, and the consuming hot drinks, spicy food, and alcohol.
It is important to have an accredited dermatologist diagnose and treat rosacea as it can often appear to be another, unrelated condition. Misdiagnosis or delayed diagnosis can result in significant discomfort and decreased quality of life for the patient. Patient education can help achieve early diagnosis and help identify particular triggers specific to the patient’s case.
- Lifestyle changes
- Medications
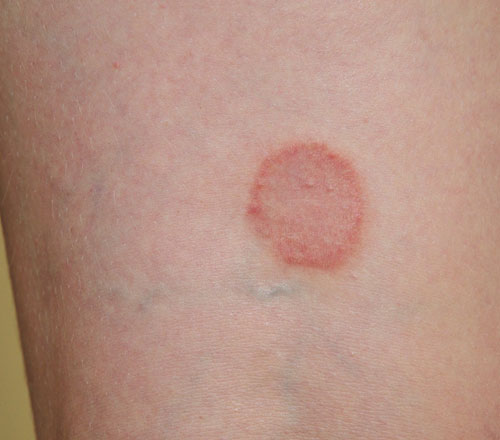
Tinea Infections
Tinea infection is an infection caused by a fungus called dermatophyte. Tinea infections spread through direct contact with the fungus organism, as well as contact with spores. A tinea infection on its own is not serious but can cause significant itch and discomfort. When left untreated, tinea infections can become infected with bacteria or yeast and lead to more severe problems in the elderly, young children, individuals with compromised immune systems, or individuals with other health problems.
Some common types of tinea infection include:
Ringworm is a fungal rash that looks like a red ring on the skin.
Athlete’s foot is most commonly affecting the skin between the toes; however, it can also affect the bottom and sides of the feet causing itching and burning. It is commonly picked up from touching damp surfaces such as shower floors, saunas, or swimming pool decks.
Jock itch affects the groin area and causes an itchy, burning rash.
Tinea infections may have similar characteristics to other skin conditions, such as granuloma annulare (non-infectious) or other dermatoses, including psoriasis or contact dermatitis.
When diagnosed correctly by a dermatologist who is specifically trained to distinguish between these skin conditions, tinea infections can be treated easily with topical medications prescribed by your dermatologist.
